A Simple Guide to Road Signs in Malaysia and What They Mean

When driving on Malaysia's roads, you will be able to see a variety of road and safety signs, with different symbols and colour schemes. While these colours and symbols may seem insignificant to you, they all have their own special meaning. In fact, Malaysian road signs are standardised based on those used in Europe, but we have our own unique distinctions.
Trying to decipher the meanings can be confusing, even for experienced drivers. Don’t worry, we’ve decoded what the different road signs mean and how they work below so you can easily navigate your way on the road.
Commonly Confused Road Signs in Malaysia
While most road signs can be easily deciphered at a glance, some are surprisingly easy to mix up, especially when you’re in a rush or when the symbols look similar. This can be dangerous, as misunderstanding a road sign can lead to missed turns, parking fines or even accidents.
Here are some of the most commonly confused Malaysian road signs and what they actually mean:
| Sign | What People Think It Means | What It Actually Means |
|
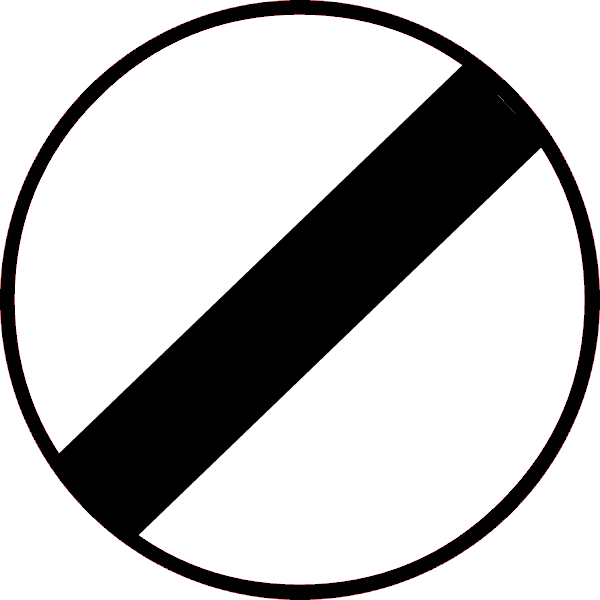
End of Speed Limit
|
Can be confused with the “No Parking” sign, as it looks similar but with a different colour scheme | Marks the end of the previous speed restrictions. You can now follow normal national limits |
|
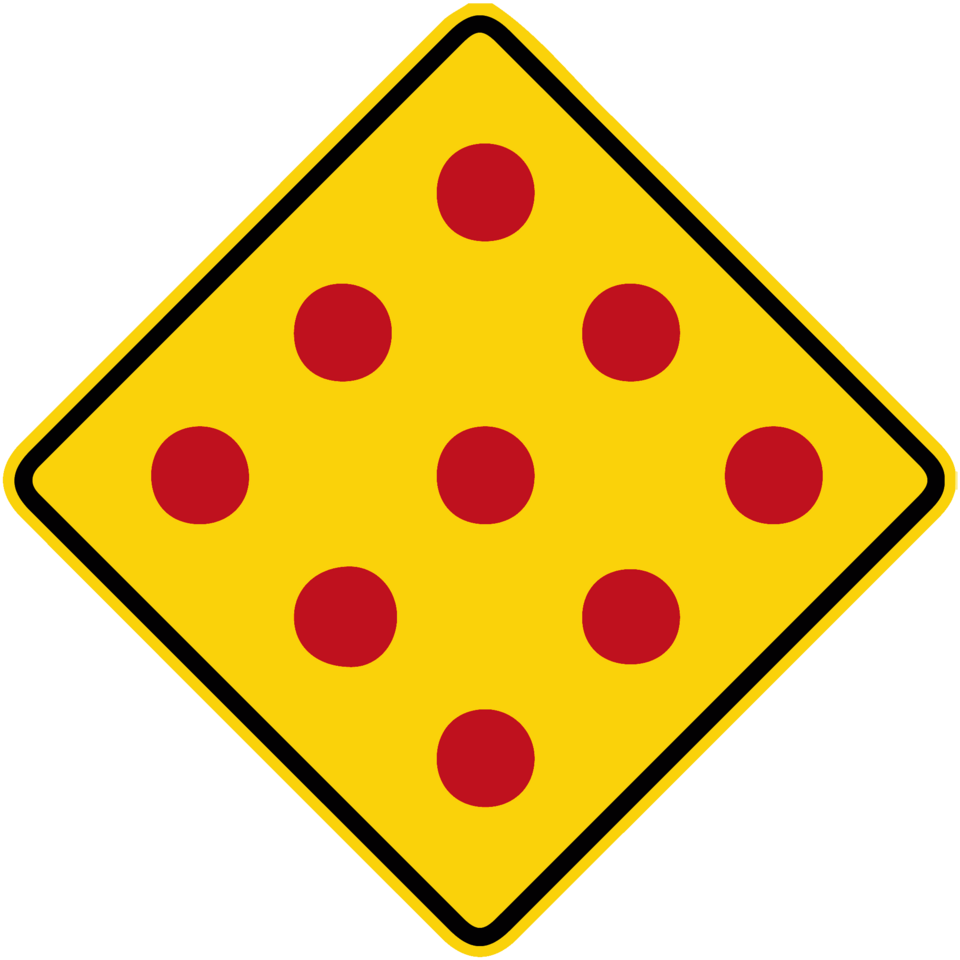
Obstacles Ahead
|
Often ignored or confused with uneven road ahead only | Warns of uneven surfaces or obstructions ahead, so drivers should slow down |
|
Divided Road Begins/Ends
|
Fork ahead or keep left or right | The road ahead indicates a section of the highway separated by a physical barrier, either beginning or ending of the road |
|
No Stopping
|
It looks almost identical to a no parking sign which has one slash but the no stopping sign has two slashes | No stopping means you cannot at all, unlike the no parking sign where you can stop briefly |
Another common confusion that can occur is when car drivers mistakenly enter motorcycle lanes. This usually happens because the road signs are unclear, too small or placed too close to junctions, so unfamiliar drivers do not notice that they have entered the wrong lane.
In addition, confusing lane design or inadequate lane separation contributes to the confusion, which can be very dangerous for legitimate motorcyclists using the lanes.
Road Sign Categories
a) Regulatory road signs

This type of road sign is arguably one of the most important types of signage in Malaysia. These road signs exist to remind and inform you about any restrictions on the road. These are usually in a red, white and black colour scheme with corresponding symbols or pictograms.
It is necessary to always follow regulatory road signs; otherwise, you may be penalised. For instance, you cannot make a U-turn when there’s a sign prohibiting U-turns or for heavy vehicles to use a particular road.
b) Mandatory road signs

Mandatory signs are used to tell road users what they must do on a specific road or direct you to the appropriate lanes, ensuring you don’t disrupt the traffic flow. It is generally circular with blue backgrounds and white symbols.
c) Speed Limit signs

Speed limit signs are there to remind you of the legal maximum speed limit for your vehicles. The colours and styles vary, depending on where the sign is located and can be part of regulatory signs or temporary signs.
d) Danger/Warning Signs
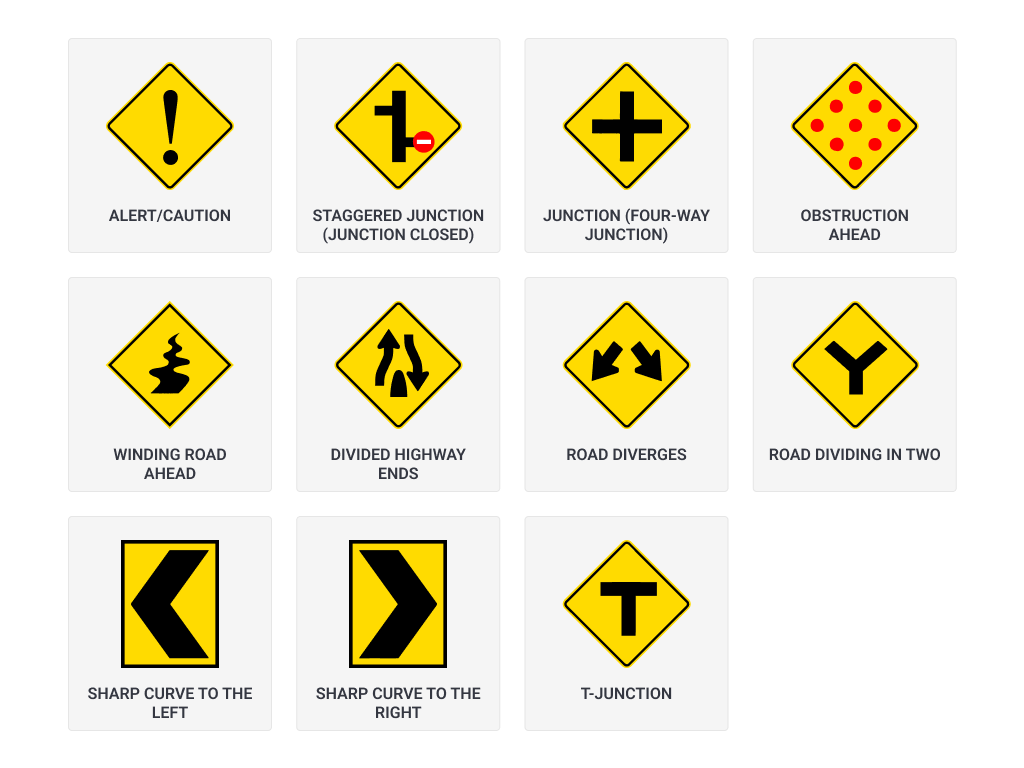

Warning signs usually come in red, yellow or black and are designed to alert you about any possible dangers or obstructions ahead. They’re usually placed before the obstruction so you can slow down and react in time.
e) Construction/Temporary Signs

These are road signs to alert you about any temporary obstructions ahead and are usually used when there’s any construction or roadworks happening. Since it is usually temporary, the signs are taken down once the planned work is finished and usually come in orange colour.
d) Information Signs

Information signs are some of the most frequently used in Malaysia to provide general or additional information about the road that they are using and the roads ahead for upcoming rest stops, bus stations, parking areas and other similar locations. These signs generally come in blue, white or green with the appropriate pictograms.
e) Guide Signs
These road signs are divided into five categories and are used to show directions or distances to a destination or road. It is usually in blue, green, brown, white, or yellow.
i. Destination Signs
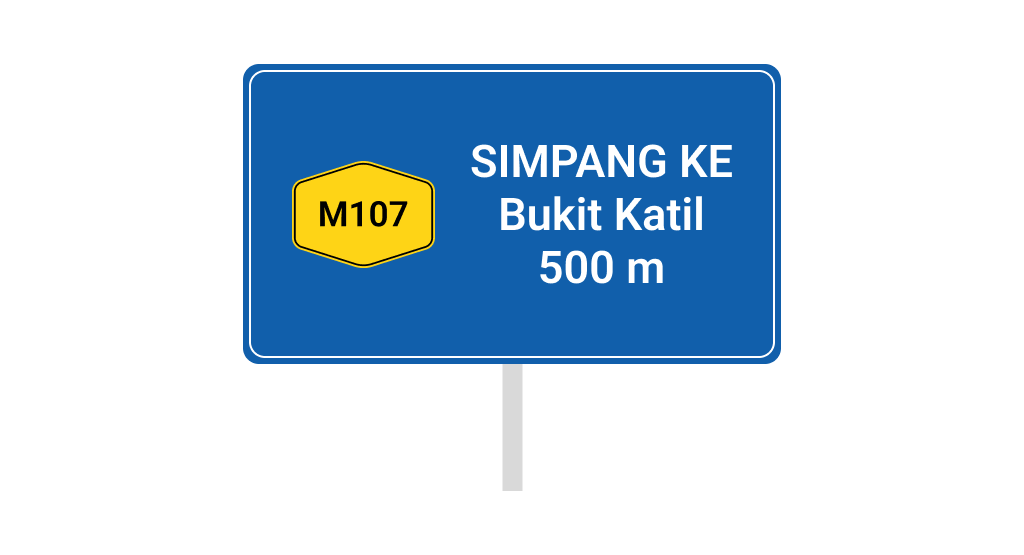
It is used to alert drivers and provide enough time for road users to move into the correct lane before reaching the intended exit or junction.
ii. Directional Signs
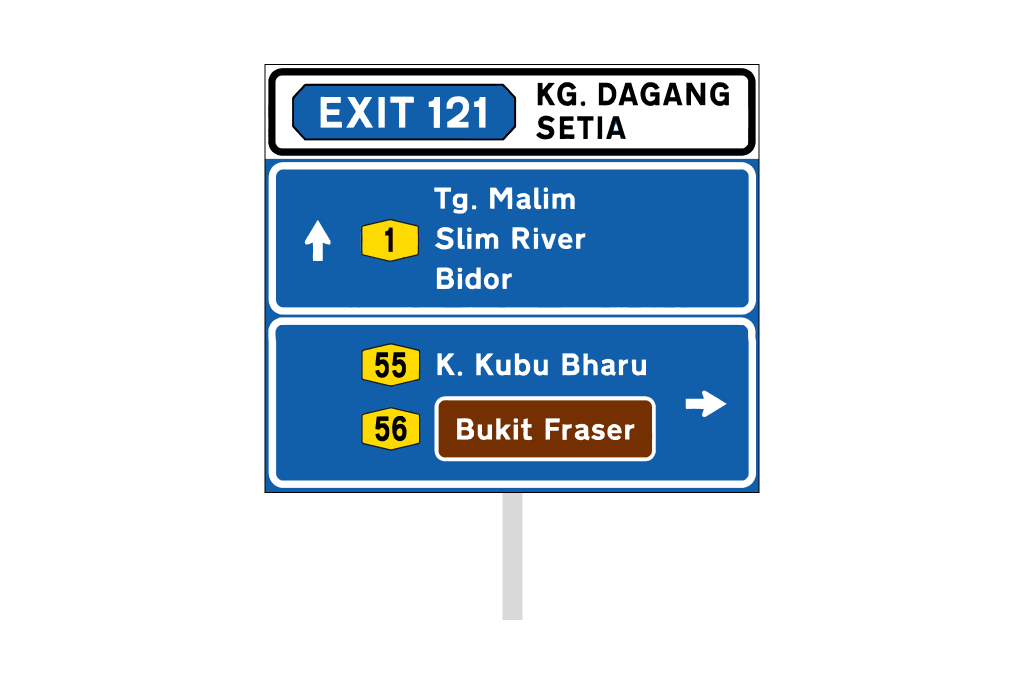
These are usually placed 100-150m before the main road or before the exit to the main road/expressway.
iii. Distance Signs
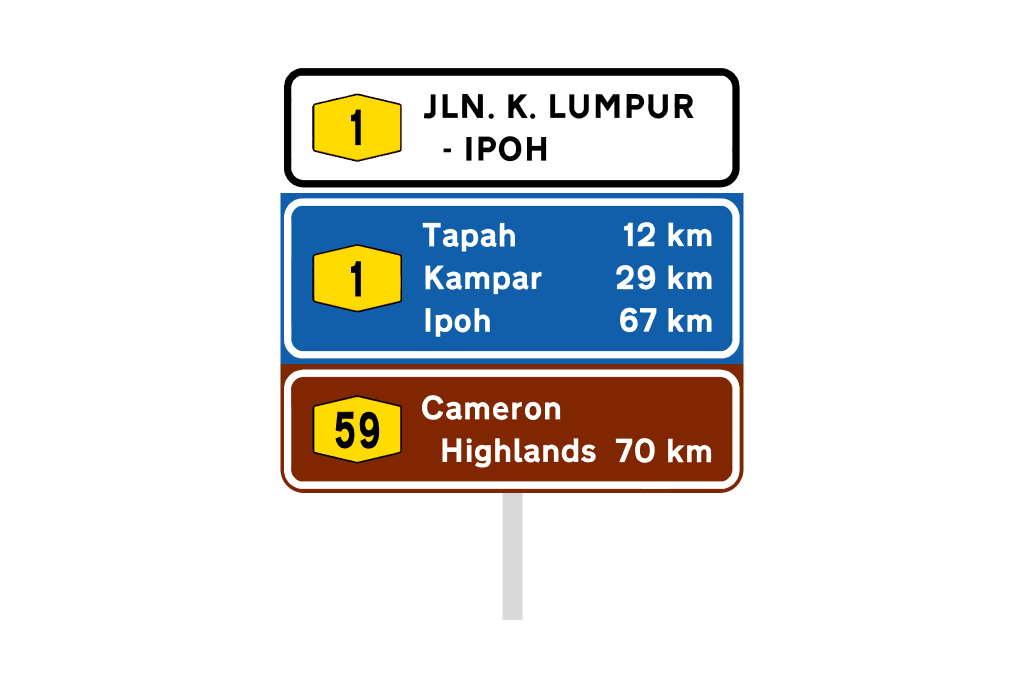
Distance signs simply indicate the distance to major destinations along the highway and are usually placed 200m after a turning roadway or 150m after the acceleration lane.
iv. Kilometre Markers
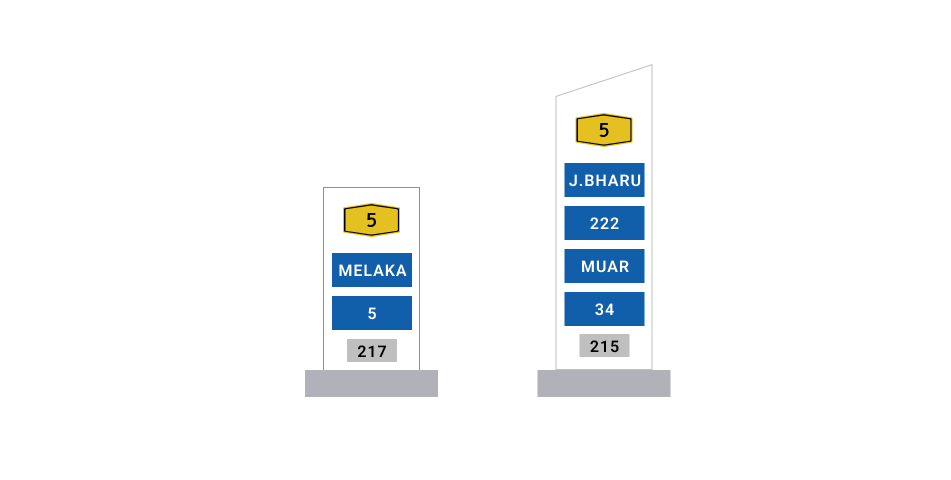
These are placed every kilometre along the entire stretch of federal and state roads for maintenance and reference purposes.
v. Route Number Signs

These signs indicate the road route numbers using a designated system of digits and prefixes. The alphanumeric combination can imply federal or state routes while the different numbers have specific meanings as well.
Other Road Sign Details You Should Know
1. Destination Placement
There is a reason for the placement of destinations on a signboard. If you notice that the road sign has different destinations, then the destination name at the top is the farthest and the one at the bottom is the nearest.
2. Colours of road signs
As you can see above, there are several different road sign colours in Malaysia. Each of them has its own meaning and is meant to indicate something to road users.
a. Blue and green signboards
The blue signboards are used for federal, state and municipal roads without tolls, with the names in white letters. Green road signs are used for expressways or highways with tolls.
b. Letters and symbols on different coloured backgrounds
- Major destinations use green backgrounds with white symbols.
- Government tourist attractions use green lettering on white backgrounds.
- Government buildings are indicated with yellow/orange lettering on green backgrounds.
- Road signs with a blue background and white lettering are used for major destinations, usually a town or area.
- Main roads used frequently are marked with road signs featuring a blue background and yellow letters.
- International and state borders in Malaysia have a green background and blue for districts.
- Towns and other settlements use a white background with black letters.
- Tourist destinations are indicated with a maroon background and white letters.
3. Symbols and shapes
You’ll find black and yellow hexagon shapes with numbers and letters on some of the road signs; these are the expressway/highway code signs.
4. Letters
The expressways are indicated with the letter E, while cycle roads use the letters CR. Federal Roads are shown using numbers and digits, for example, Federal Route 1. However, federal road numbers can also be added with the FT—prefix before the route number, which means Federal Route 1 can also be known as FT1. Meanwhile, state roads use both letters and numbers, except for the letter 'E'.
Conclusion
Road signs are crucial in keeping Malaysian roads safe and organised. After understanding the various road signs, drivers can make quicker and safer decisions while driving. Remember to keep an eye out while driving, as these guides ensure that the roads remain safe for everyone.
Disclaimer: The information in this blog post is provided solely for the purpose of promoting awareness and understanding among road users. It is strictly for informational purposes and should not be taken as advice of any kind.
While every attempt has been made to ensure accuracy, it should not be considered as a substitute for official road regulations or legal advice. For complete and up-to-date information, readers are encouraged to refer to the official road rule book or relevant traffic authority guidelines. Kurnia disclaims all responsibility for any losses resulting from reliance on the information contained in this article.



